Prostate cancer is a type of cancer that affects the prostate gland, a small, walnut-shaped organ located just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It is the second most common type of cancer among men in the United States and about one in nine men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer in their lifetime.
Table of Contents
Risk Factors for Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a complex disease that can be caused by a combination of factors. Understanding these risk factors can help men make informed decisions about their health and seek regular screenings. The most common risk factors for prostate cancer are as follows:
- Age: Most prostate cancer cases are diagnosed in men over the age of 65.
- Race: African American men are more likely to be diagnosed with prostate cancer than men of other races, and their tumors are also more likely to be aggressive. Whereas Asian, Hispanic, and Native American men have a lower risk of developing this disease.
- Family History: If a man has a father or brother who has had prostate cancer, his risk of developing the disease is two to three times higher than average.
Signs & Symptoms of Prostate Cancer
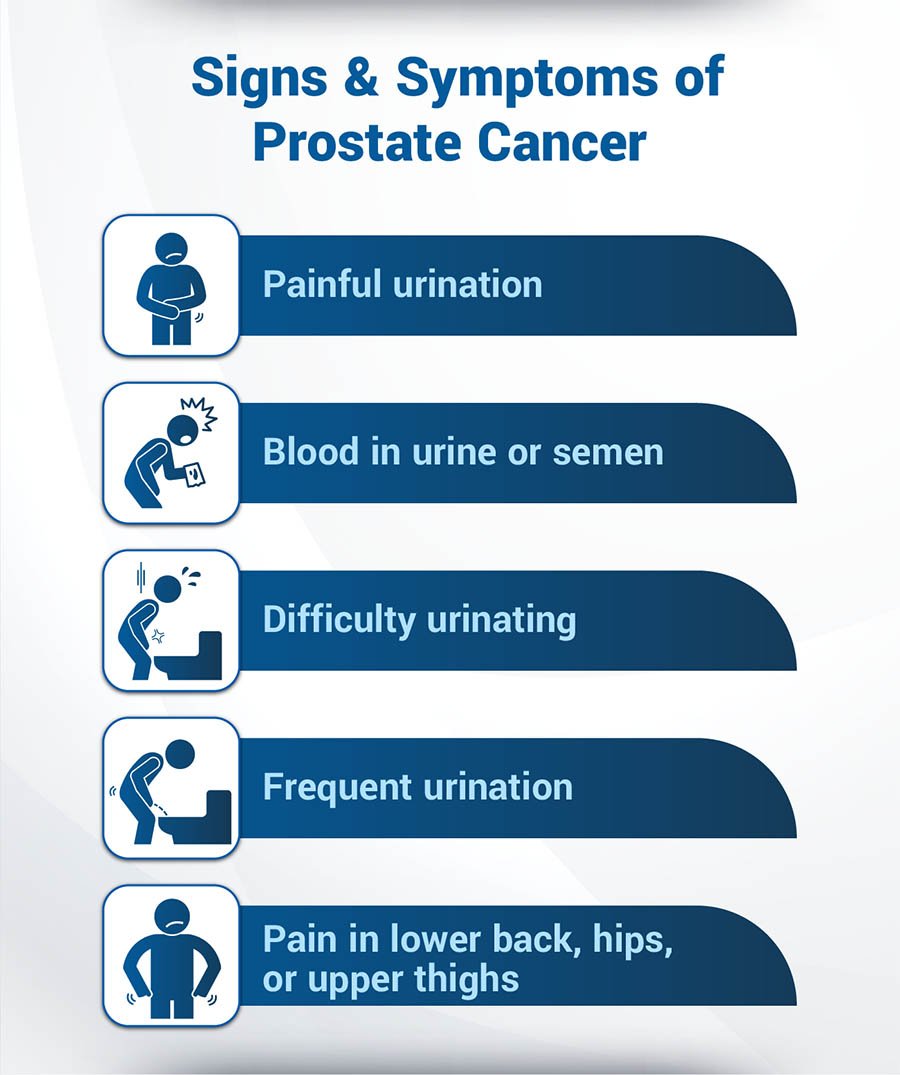
Prostate cancer is slow-growing cancer, and often there are no visible symptoms in the early stages of the disease. Nevertheless, it is crucial to be aware of the symptoms for prostate cancer detection and to discuss any concerns with a healthcare provider. The following are a few warning signs of prostate cancer:
- Difficulty urinating:
If a person is having trouble during urination, it indicates a weak urine stream which can be a symptom of prostate cancer.
The prostate gland surrounds the urethra, a tube that carries urine from the bladder to the outside of the body. If the prostate gland is enlarged or cancerous, it can put pressure on the urethra and cause issues during urination.
- Painful urination
Also known as dysuria, painful urination can indicate prostate cancer. Pain during urination can be caused by an inflamed or infected prostate gland, or by cancer itself.
- Blood in urine or semen
Although it is more commonly a sign of other conditions, such as a urinary tract infection or an enlarged prostate, blood in urine or semen can also indicate cancer.
- Frequent urination
The urge to urinate frequently, especially at night, can be a symptom of prostate cancer. The enlarged or cancerous prostate gland puts pressure on the bladder and creates a need to urinate more frequently.
- Pain in the body
If the cancer has spread beyond the prostate gland, it can cause pain in the lower back, hips, or upper thighs.
In addition to the symptoms listed above, there are a few other signs and symptoms that may indicate prostate cancer, including:
- Fatigue and weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Erectile dysfunction
- Urinary incontinence
However, these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions and are not always a sign of prostate cancer. If an individual is experiencing any of these symptoms, it is wise to consult with a healthcare provider.
Prostate Cancer Diagnosis
Physical exam
This is the first step in prostate cancer diagnosis. During a physical exam, the healthcare provider will feel the prostate gland to check for any abnormalities, such as lumps or hardness. This medical procedure is commonly known as a digital rectal exam (DRE).
Imaging Tests:
These tests can help to confirm a diagnosis of prostate cancer or to determine the extent of the disease. The most common imaging tests used in the diagnosis of prostate cancer are as follows:
- Ultrasound: This imaging test uses sound waves to create images of the prostate gland. It helps determine the size and shape of the gland and identify any abnormalities.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): It uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to create detailed images of the prostate gland and identify the extent of the disease.
Biopsy
This diagnostic test is the only way to confirm a diagnosis of prostate cancer. During this procedure, a small sample of tissue is taken from the prostate gland and examined under a microscope to detect the presence of cancerous cells.
To receive personalized treatment and cancer care for prostate cancer, contact Advanced Cancer Treatment Center and schedule an appointment.
How to Prevent Prostate Cancer
Although there is no guaranteed way to prevent prostate cancer, there are steps one can take to minimize their risk. These include:
- Avoid red and processed meat
Red and processed meat contain high levels of saturated fat, which can increase production of hormones linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer. Besides, processed foods are also a source of dietary iron, which has been linked to oxidative stress. Therefore, excessive intake can lead to cellular damage and the development of cancer.
Add more fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole to your diet to increase the number of antioxidant-rich foods in diet. These foods can help protect cells from oxidative stress and reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
- Stay physically active
Regular physical activity can help regulate hormones and reduce levels of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) hormones which are linked to an increased risk of prostate cancer. In addition, exercise can also help maintain healthy weight, which is important for reducing the risk of this disease.
A combination of aerobic exercise and resistance training are particularly effective in reducing the risk of prostate cancer. Aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, jogging, cycling, or resistance training, such as weightlifting, or resistance band exercises are extremely useful in the prevention of prostate cancer.
- Do not smoke or drink
Smoking tobacco can increase the risk of prostate cancer by exposing the body to harmful chemicals that can damage DNA and lead to cellular mutations. In addition, heavy drinking has been shown to increase levels of cancer-causing hormones, leading to oxidative stress and cellular damage. Therefore, it is wise to avoid smoking or drinking to reduce the risk of prostate cancer.
Conclusion
Regular screening is important for early detection of prostate cancer and the treatment of the disease. Prostate cancer often has no symptoms in its early stages, making regular screening tests crucial for detecting the disease before it progresses. Also, if someone experiences these symptoms, they should consult a healthcare provider at the earliest for early detection.