Table of Contents
Introduction to Hardware Wallets
Cryptocurrencies have brought a new era of financial freedom, but with it comes the responsibility of ensuring the security of your digital assets. Hardware wallets are physical devices that store your cryptocurrency keys offline, providing a high level of security against hacking and theft. This guide aims to provide a comprehensive overview of hardware wallets and how they can help you keep your crypto safe. Quantum Lumina Site offers a user-friendly interface and robust security features, making it a reliable choice for storing your cryptocurrency keys offline.
How Hardware Wallets Work
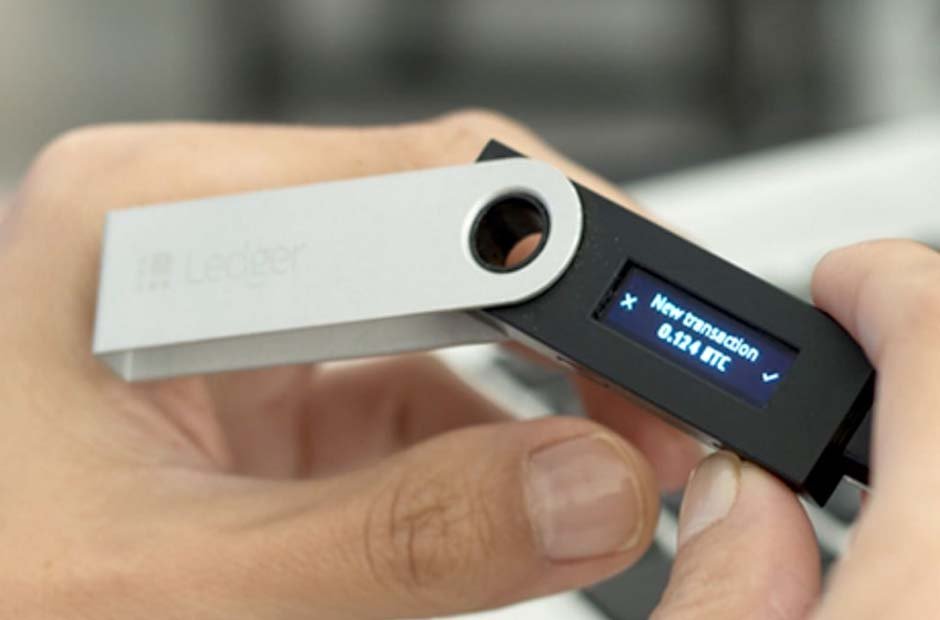
Hardware wallets work by generating and storing your cryptocurrency keys offline, away from potential threats such as malware and hackers. They typically consist of a secure element (a chip designed for storing cryptographic keys) and a display for interacting with the device. When you want to send cryptocurrency, you connect the hardware wallet to a computer or mobile device and authorize the transaction using the device’s buttons.
Types of Hardware Wallets
There are two main types of hardware wallets: USB-based wallets and smart card-based wallets. USB-based wallets are similar in appearance to USB flash drives and are connected to a computer or mobile device via a USB port. Smart card-based wallets, on the other hand, are the size of a credit card and are inserted into a smart card reader for use.
Popular brands of hardware wallets include Ledger, Trezor, and KeepKey. These wallets offer varying levels of security and features, so it’s essential to research and choose one that meets your needs.
Setting Up a Hardware Wallet
Setting up a hardware wallet is a straightforward process:
- Unboxing: Open the package and ensure that all components, including the device, cable, and instruction manual, are included.
- Connecting: Connect the hardware wallet to your computer or mobile device using the provided cable.
- Initialization: Follow the on-screen instructions to initialize the device and set up a PIN code.
- Backup: Write down the recovery seed (a series of words) provided by the device and store it in a safe place. This seed is used to recover your wallet if the device is lost or damaged.
Using a Hardware Wallet
Once your hardware wallet is set up, you can use it to send and receive cryptocurrency:
- Receiving Crypto: Obtain your wallet’s receiving address and provide it to the sender to receive cryptocurrency.
- Sending Crypto: Connect your hardware wallet to a computer or mobile device, open the wallet application, and follow the instructions to send cryptocurrency.
Hardware wallets also offer additional features, such as support for multiple cryptocurrencies and integration with software wallets for added convenience.
Security Best Practices
To ensure the security of your hardware wallet and cryptocurrency, follow these best practices:
- Use Strong Passwords: Set a strong, unique password for your hardware wallet and avoid using it on other websites or devices.
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication: Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on your accounts for an added layer of security.
- Keep Your Recovery Seed Secure: Store your recovery seed in a safe place, such as a safe or a secure location, and avoid storing it digitally.
- Regularly Update Your Device: Keep your hardware wallet’s firmware and software up to date to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Recovering Your Hardware Wallet
If your hardware wallet is lost or damaged, you can recover access to your cryptocurrency using the recovery seed:
- Obtain a New Device: Purchase a new hardware wallet of the same brand and model as your old one.
- Initialize the New Device: Follow the instructions to initialize the new device and set up a new PIN code.
- Enter the Recovery Seed: During the setup process, you will be prompted to enter your recovery seed. Enter the seed to recover access to your cryptocurrency.
Conclusion
Hardware wallets provide a secure and convenient way to store your cryptocurrency keys offline, protecting them from hacking and theft. By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can keep your crypto safe and secure.